
One way to distinguish between leaders and laggards in an industry is through supply chain optimization. In 2023, the worldwide supply chain management market is expected to be worth $15.85 billion. By 2027, it is anticipated to have grown at an incredible CAGR of 11.2% to reach an astounding $37.4 billion.
Table of Content
Even with this rapid expansion, problems still exist.
Last year, a startling 74% of businesses reported major supply chain interruptions, which cost them an average of $184 million a year in lost income, higher expenses, and harm to their reputation.
Generative AI can help in this situation. Logistics and supply chain operations are being transformed from reactive cost centers into proactive strategic benefits by this technological advancement.
Generative AI represents a fundamental evolution beyond traditional artificial intelligence. The conventional AI systems excel at analyzing historical data and identifying patterns. However, generative models create entirely new outputs, solutions, and scenarios that didn’t previously exist.
For supply chain leaders, this distinction is critical. Traditional analytics might tell you what happened and why. But generative systems tell you what could happen next and recommend optimal courses of action.

Let’s look at the core technologies powering this revolution:
that understand natural language queries about inventory, logistics, and planning
that process complex multi-dimensional supply chain data
that continuously optimize based on outcomes
capabilities that enable scenario planning
Basically, these technologies work in concert to transform how goods move from manufacturing to end consumers. Hence, creating efficiencies previously impossible with human analysis alone.
The financial impact of Generative AI in supply chain operations is clear and compelling. Here’s how:
And these aren’t speculative projections – they’re real results from early adopters across retail, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods industries.
In a McKinsey study of Gen AI implementation, supply chain operations showed the highest ROI compared to other business functions, with 85% of pilot projects delivering positive returns within 12 months.

Traditional demand forecasting has long been the Achilles’ heel of supply chain management. With error rates averaging 30-40% in many industries, the consequences are severe. From excess inventory, stockouts, to customer dissatisfaction- the list is long.
Forecasting is revolutionized by generative AI, which analyzes thousands of variables at once. It includes both obvious elements like past sales and seasonality as well as more subtle ones like sentiment on social media, weather trends, and macroeconomic data.
The results are striking. Companies implementing Gen AI for demand planning report:
These improvements deliver both immediate cost savings and long-term competitive advantages through enhanced customer experiences.
Next, inventory represents one of the largest capital investments for most companies. Traditional inventory management relies on rules-based systems with minimal adaptability.
Generative AI brings dynamic intelligence to inventory decisions through:
The technology creates customized inventory policies that evolve continuously, reducing carrying costs while maintaining or improving service levels. Companies typically report 27% reductions in carrying costs while simultaneously increasing product availability.

Supply chain disruptions have become the new normal – from pandemic effects to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and labor shortages. Indeed, traditional risk management approaches struggle to keep pace.
Generative AI transforms risk management through:
Organizations using Gen AI for network resilience report 42% fewer disruption impacts and 68% faster recovery times when incidents occur.
This capability translates directly to the bottom line – companies with more resilient supply chains achieve 7-10% higher shareholder returns compared to industry peers.
The transportation costs typically represent 8-10% of a product’s final price. This makes logistics optimization a critical competitive lever.
Traditional routing systems work with static plans and limited variables. Generative AI revolutionizes this approach by:
These upgrades can boost service quality and sustainability indicators while also saving millions of dollars a year for a mid-sized logistics company.
The modern warehouse represents a complex orchestration of human workers, automation technology, and inventory movement. Generative AI serves as the central nervous system of this environment.
The technology transforms warehouse operations by:
These benefits position the warehouse as a strategic advantage rather than merely a cost center in the supply chain.
Supplier relationships directly impact supply chain performance across quality, cost, and reliability dimensions. Generative AI transforms procurement functions through:
These skills offer vital competitive advantages in a global market where supply networks are becoming more intricate.
Environmental effect is becoming a business-critical priority rather than a side issue. Supply chain sustainability has a direct impact on competitive positioning, as 73% of consumers take sustainability into account when making purchases and regulatory demands are growing.
Generative AI optimizes supply chains for both profit and environmental impact by:
Companies implementing these capabilities report:
The sustainability paradox – better environmental performance driving better financial performance – becomes achievable through AI-powered optimization.

While the benefits of Generative AI in supply chain operations are compelling, implementation requires strategic planning and careful execution. Here’s a comprehensive roadmap to guide your journey from concept to operational reality.
Start by carefully assessing how your supply chain is currently operating. Keep track of problems, inefficiencies, and situations where judgment is primarily based on gut feeling rather than facts. The basis for gauging upcoming advancements is this baseline evaluation.
The most important success criteria for any Gen AI implementation is data readiness. Perform a thorough data audit that addresses governance, accessibility, quality, and availability. Before implementing advanced AI, many firms find important holes in their data infrastructure that need to be fixed.
Create a cross-functional team of business executives, data scientists, supply chain specialists, and IT specialists. Throughout the implementation process, this diversified team makes sure that technological capabilities match business objectives.
Prior to starting the technical implementation, establish precise success measures. Hard financial metrics (cost cutting, inventory efficiency) as well as operational enhancements (predictability, delivery performance) ought to be part of these.
Rather than attempting a comprehensive transformation, identify a specific high-value use case for your initial implementation. Ideal pilot projects provide meaningful business impact while remaining contained enough for rapid execution.
Popular starting points include:
Structure your pilot as an 8-12 week sprint with clear milestones and evaluation criteria. This schedule strikes a compromise between the complexity of implementation and the requirement for speedy outcomes.
Keep technical teams and business stakeholders informed at all times during deployment. Alignment is ensured and new issues are addressed through weekly progress evaluations and adjustment sessions.
Following pilot completion, conduct a rigorous evaluation against your predefined success metrics. Document both quantitative improvements and qualitative insights gained through the implementation process.
Most organizations discover their initial implementation delivers both expected benefits and unexpected advantages in adjacent processes. Catalog these discoveries for potential expansion opportunities.
Based on pilot results, develop a phased scaling plan that prioritizes high-value use cases across your supply chain operations. This typically follows a pattern of:
Throughout scaling, continue investing in change management and training. The human element often proves more challenging than technology implementation, particularly as AI capabilities expand across the organization.
While the benefits of Generative AI in supply chain are compelling, organizations should be aware of common challenges that can impact implementation success.
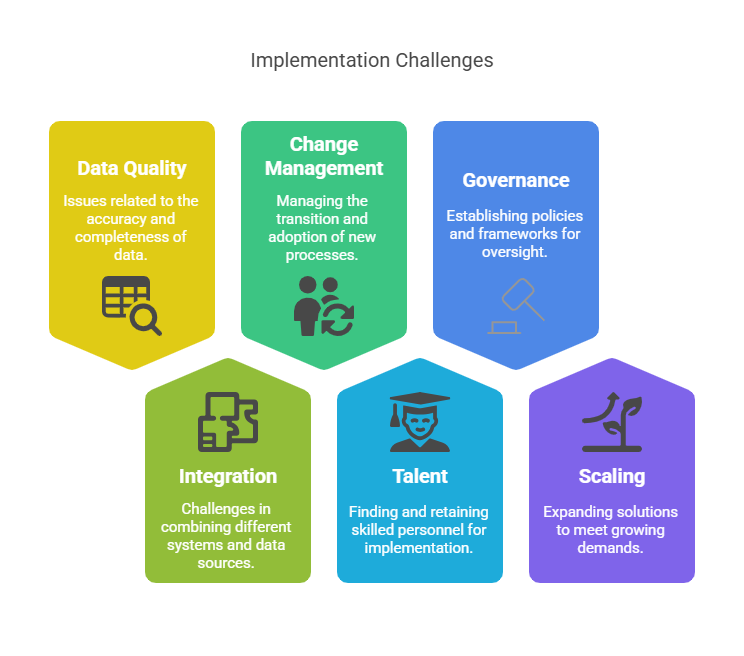
Generative AI systems require large volumes of clean, accessible data to deliver optimal results. Many organizations discover significant data gaps during implementation, including:
Before fully implementing AI, addressing these problems frequently calls for committed work. Before moving forward with advanced AI projects, businesses should assess their data preparedness and fill in any important gaps.
Most supply chains rely on a complex network of pre-existing systems, including ERP platforms, warehouse management systems, planning tools, and transportation management systems. Generative AI must be compatible with these systems in order to be useful.
Integration challenges commonly include:
Successful implementations typically include dedicated integration resources and sometimes require middleware solutions to bridge technology gaps.
The human element of Generative AI implementation often proves more challenging than the technology itself. Supply chain professionals must adapt to new ways of working that leverage AI insights while applying human judgment to decisions.
Critical people-related considerations include:
Organizations that invest equally in technology and people achieve significantly better results than those focusing exclusively on technical implementation.
The Generative AI revolution in supply chains is just beginning. Several emerging trends will shape the evolution of these technologies over the next 3-5 years:

Next-generation supply chain AI will combine multiple data types – text, images, sensor readings, and structured data – into unified models. This enables more comprehensive understanding of complex supply chain environments.
Applications include:
These multimodal capabilities will deliver more intuitive interfaces and deeper insights than today’s primarily text and data-based systems.
The convergence of Generative AI with digital twin technology will create complete virtual replicas of physical supply chains. These digital environments enable:
Organizations will increasingly run thousands of simulations before implementing changes in their physical supply chains, dramatically reducing implementation risk.
While current Generative AI systems primarily provide recommendations for human decision-makers, autonomous capabilities are expanding rapidly. Future systems will directly execute routine decisions while escalating exceptions for human judgment.
This progression will occur gradually across decision types:
The human role will evolve toward exception handling, strategic oversight, and relationship management as AI systems handle increasing operational complexity.
Environmental considerations will become increasingly integrated into all supply chain decisions. Generative AI will optimize simultaneously for traditional metrics (cost, service, quality) and sustainability impacts.
Advanced capabilities will include:
Organizations that lead in this integration will gain advantages in both operational efficiency and market positioning.
Generative AI is more than just a small-scale enhancement of current procedures; it signifies a major change in supply chain capabilities. Businesses who understand this shift and take action will gain long-term competitive advantages.
Our area of expertise is creating unique generative AI solutions for supply chain and logistics management. At whatever point in an organization’s AI journey, our team of supply chain professionals and AI specialists collaborate to produce disruptive outcomes.
Our strategy ensures solutions that address actual business difficulties rather than merely installing technology for its own sake by fusing in-depth technical competence with real-world supply chain knowledge.
Code Brew’s supply chain AI services include:
Remarkable outcomes, such as 25% inventory reductions, 30% increases in forecast accuracy, and millions in transportation cost savings, have been attained by companies in the retail, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, and consumer products sectors.
Whether you’re just beginning to explore AI capabilities or looking to scale existing pilots, Code Brew provides the expertise, technology, and support to transform your supply chain operations into a genuine competitive advantage.
